A genus of at least 300 dioecious, woody species, ranging from large trees to prostrate creeping shrubs. It is found in all continents except Australasia but largely in the cooler latitudes and altitudes of the northern hemisphere, including alpine and arctic regions. The leaves are deciduous, very variable in shape, entire or toothed, usually short stalked and, with rare exceptions, arranged alternately on the twigs. The inflorescence is in the form of a cylindrical (or occasionally globular) catkin, in which the flowers are arranged around a central axis each being subtended by a small scale or bract. There are no petals. The male flower consists of stamens, usually two, sometimes fused together in the lower part, and one or two small glands or nectaries which may be united into a ring. In the female flower the stamens are replaced by a flask shaped ovary with style (often divided) and stigmas. When ripe the ovary splits into two carpels, discharging the very small seeds, each with a tuft of silky hairs. The catkins may be sessile or borne on the end of short leafy shoots and may appear before, with or after the leaves.
The smaller species are suitable for the rock garden, scree, raised bed or trough. Most small species also respond easily to pot culture, but their character is best expressed when they are given a wide root run. In general willows are easy to cultivate provided they are not subjected to deep shade or dryness at the root. Propagation is easily effected in nearly all cases by means of cuttings either of softwood (with or without a heel of old wood) taken in early to mid summer or of hard wood taken after leaf fall in the autumn. Seed has a very short period of viability and does not provide a convenient means of propagation, but plants, in particular hybrids, may be raised by sowing very fresh seed directly from the ripening female catkin. It should be sown on the surface of constantly moist soil in a well lit position.
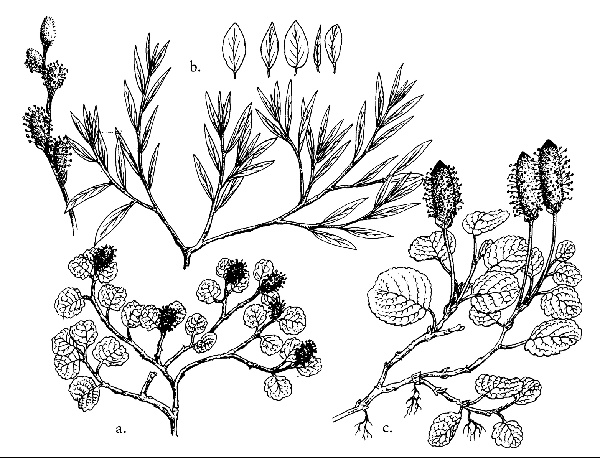
a, S. herbacea; b, S. repens; c, S. reticulata;
Sign up for our newsletter to receive our monthly update direct to your inbox. Featuring our latest articles and news.
Built by Atomic Smash

